July 27, 2006
Financial Services Agency
Government of Japan
The Basic Policy and Plan for Financial Inspections in Program Year 2006
The FSA announced today its Basic Policy and Plan for Financial Inspections in Program Year (PY) 2006.
* ''Program year 2006'' refers to the period from 1 July 2006 through 30 June 2007
Contact
Financial Services Agency, Government of Japan
Tel +81-(0)3-3506-6000 (main)
Inspection Coordination Division, Inspection Bureau (ext. 2535,2524)
(Provisional translation)
Basic Policy and Plan for Financial Inspections in Program Year 2006
I. Basic Policy for Financial Inspections in Program Year (PY) 2006
The Financial Services Agency (FSA), in accordance with the Program for Further Financial Reform, aims to establish the financial system that provides the high level of the satisfaction of customers and that is highly evaluated across the world. The FSA is conducting its inspection, emphasizing the two-way dialogues between the financial institutions and inspectors in accordance with the Financial Inspection Basic Policy (FIBP), which was established in July 2005, and also making efforts to make the new inspection rating system ''Financial Inspection Rating System (FIRST)'' more familiar to the financial institutions.
For PY 2006, the FSA will carry out its inspections in both proper and effective manners to ensure the soundness and the properness of the management of the financial institutions, while paying attention to the change of the environment surrounding them, such as growing need for customer protection and the implementation of New Basel Capital Accord (the new capital adequacy framework).
1. The Basic Concept for management of Financial Inspection
The FSA has been conducting its inspections in line with the FIBP to ensure the transparency. For PY 2006, the FSA will try to improve methods of inspection, taking into account the opinions filed through inspection monitoring system. Also, the FSA will try to keep two way dialogues between the financial institutions and the inspectors, and to implement proper inspections emphasizing the process check of the internal control of the financial institutions as well as examining the appropriateness of the specific issues.
When conducting inspections, the FSA will focus on a specific area according to the characteristic and the financial condition of the financial institutions. Also, the FSA will determine the coverage and depth of the inspection due to the effectiveness of their internal auditing so as to enhance the efficiency and the effectiveness of inspections. The FSA will develop the efficiency of inspections by utilizing the advanced electronic devises. Moreover, in order to enhance the effectiveness of inspections, the Inspection Bureau of the FSA will develop closer coordination with the Supervisory Bureau, as well as with the Local Finance Bureaus.
On the other hand, the FSA has started the trial implementation of the FIRST since January 2006. The FSA and the Local Finance Bureaus have been gathering the data and providing adequate training sessions to all our inspectors. The FSA has published the Q & A for the FIRST in March 2006, and also published the sample finding examples related to the inspection ratings in July. The FSA will officially implement the FIRST in the near future, considering the trial situation.
2. Priorities in Inspection
The FSA will examine the compliance and the risk management of the financial institutions, emphasizing further focus on their internal control as well as examining the appropriateness of specific transactions.
There are various challenges that the financial institutions should tackle. Thorough customer protection and advanced risk management have been further required because of the recent diversification of investment management and the fluctuation of the interest rates. The management of the financial institutions is required to develop more proper internal control, including internal auditing in order to tackle those challenges.
(1) Thorough Customer Protection
The FSA, considering the newly enacted Financial Instruments and Exchange Law, will examine the efforts by the financial institutions for their customer protection to ensure the thorough customer protection in the financial transactions. Also, the FSA will continuously make utmost use of the information filed with the Financial Customer Services Center established within the FSA in July 2005 in addition to that filed with the Inspection Information Desk.
i)Responsibility for customers (accountability, fulfillment of contracts)
a)Performance of Accountability
Since financial products are diversified and become more complicated, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions are fulfilling the accountability to their customers, in order to enable depositors, policyholders and investors to make transaction with their understanding of various risks such as those of derivative deposits, insurance products and investment trust products. Also, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions abuse their dominant position to their borrowers, or whether they explain the legal responsibilities and relevant risks to the guarantors when they seek to obtain their guarantees for loans. In this case, the FSA will emphasize the verification of the appropriateness of their way of explanation to the customers from the view point of process-checking.
As to the non-banking money lenders, the FSA will examine whether they fully explain the details of the contracts to the borrowers and guarantors, and develop proper measures to ensure customer protection.
b)Fulfillment of contracts (insurance and trust contracts)
As to the insurance contracts, the FSA will examine the promptness and the adequacy of insurance payment management, and also the adequacy of insurance contract management, including the fair deal with the cancellation and lapse of contracts.
As to the trust contracts, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions properly manage the entrusted assets by fulfilling the necessary duties such as fiduciary duty of loyalty.
ii)Due processing of customer complaints
In light of many problems with the customer complaints processing, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions properly process the complaints from customers, report them to the management, analyze the causes of them and promptly consider appropriate corrective actions to prevent similar problems.
iii)Ensuring the safety of financial transactions
Under the Depositor Protection against Counterfeited and Stolen ATM Cards Law, the FSA will examine whether the banks ensure the safety of their ATM systems and implement appropriate actions against the abuse of cash cards or the illegal access through internet.
iv)Customer data protection
The FSA continues to examine the customer information management by the financial institutions, based on the situation that there are still many problems in the treatment of customer data.
v)Proper disclosure
Since the deposit insurance system was amended in April 2005, the financial institutions have been required to strength their management under market discipline by developing their disclosure. Also, the necessity of proper disclosure is specified in the PillarIII of the new Basel Capital Accord. Taking account of this situation, the FSA will examine the adequacy of their disclosure.
(2) Examination of diversification of risk and advance of risk management
The FSA will properly respond to the diversification of risk and the advance of the risk management of financial institutions.
i)Diversification of risk
The way of asset management has become more diversified, such as investment in hedge funds, real estate funds and structured bonds, and non-recourse real estate loans, syndicated loans and structured loans. In addition, complicated and advanced transactions, such as securitization, liquidation and investment banking business have been significantly growing. Under such conditions, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions develop the appropriate Asset and Liability Management (ALM) with considering probable interest rate fluctuations. Also, the FSA will examine whether they develop proper risk management functions for specific assets.
ii)Integrated risk management
The recent growing diversity and complexity of risk require the responsibility of the financial institutions for voluntarily developing their risk management. Under such circumstances, the FSA will examine whether they adequately develop the integrated risk management in accordance with their size and risk profile.
iii)Inspection under the New Basel Capital Accord
In view of the implementation of the New Basel Capital Accord in March 2007, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions properly calculate the capital ratio based on the New Accord and adequately evaluate their level of capital. In addition, the FSA will examine the efforts by the financial institutions for improving their integrated and individual risk management that are required by the New Accord. The FSA will revise its Inspection Manuals to respond to the implementation of the New Accord.
(3) Examination based on globalization and structural changes in financial services
The FSA will properly respond to globalization and structural changes in financial services, increase of outsourcing and participation of new-form financial institutions.
i)Considering recent financial conglomeratization, the FSA will examine the integrated risk management system of the financial conglomerates. As to the securities firm that forms a part of financial conglomerate, the Inspection Bureau of the FSA will conduct joint inspection with the Securities and Exchange Surveillance Commission as needed. The FSA itself will conduct the inspection of non-banking money lenders that are inspected by Local Finance Bureaus so far. Furthermore, the FSA will examine whether the financial institutions properly manage their overseas operations so as to ensure the proper risk management and the compliance with the laws and regulations in foreign countries where those financial institutions operate their business.
ii)Taking into account the implementation of the Recommendations by the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF), the FSA will examine the efforts by the financial institutions for preventing money laundering and for the compliance with the Customer Identification Law.
iii)Taking into account the growing trend and the diversification of outsourcing by the financial institutions, the FSA will examine how they manage and monitor the outsourced services. The FSA, as needed, will examine the trustee companies, and also will examine the bank agencies and the small-claims and short-term insurance companies that are newly established in accordance with the enactment of amended Laws in April 2006.
(4) Examination of small business financing
In order to support the revival of small-and medium-size enterprises(SMEs) and the revitalization of regional economies through strengthening the regional financial functions, the FSA, considering how the regional financial institutions (RFIs) evaluate the conditions of the regional SMEs, will examine the efforts by the RFIs for the revitalization of the SMEs.
i)Inspection, considering the actual condition of SMEs
The FSA, considering the actual condition of the SMEs, will examine the asset classification of the loans to the SMEs in accordance with ''The Supplement to the Financial Inspection Manual: Treatment of Classifications regarding Credits to Small and Medium-Size Enterprises''. In addition, the FSA will ensure the proper implementation of the inspection of RFIs by utilizing the opinions filed through the inspection monitoring.
ii)Examination of the efforts by RFIs for revival of SMEs
The FSA will examine to what extent RFIs are making their efforts for supporting the revival of local SMEs in line with ''The Supplement to the Financial Inspection Manual''.
3. Priorities in specific financial sectors
In addition to the general priorities in inspection stated above, the FSA will conduct the inspection of each financial sector, based on the following specific priorities.
(1) Deposit-taking financial institutions
As to the deposit-taking financial institutions, the FSA will examine the efforts by them for customer protection, specifically how they fulfill accountability to the customers. The FSA will also examine the credit risk management including that for large debtors, and market risk management according to their scale or characteristics.
(2) Trust banks
As to the trust banks, there are some problems in the review of the entrusted assets when they liquidate the real estates. The FSA will thus examine in line with the Inspection Manual for Trust Banks whether they establish the proper system for the review of entrusted assets, and that for asset management so as to avoid the conflict of interest.
(3) Insurance companies
It is very important and fundamental for the insurance companies to properly sell insurance products and appropriately make payments of insurance claim.
The FSA, in line with the Inspection Manual for Insurance companies revised in June 2006, will examine how the insurance companies protect their policyholders, specifically how they manage their sales and payments.
In addition, the FSA will examine their soundness, actuary functions, product development and their risk management as well as the internal control system and compliance.
(4) Foreign financial institutions
As to the foreign financial institutions, the FSA, considering the above stated inspection priorities of each financial sector, will examine their compliance with the laws and regulations in Japan and the overall risk management of their financial group. The FSA will also examine whether they properly manage their new business such as private banking from the view point of customer protection.
(5) Non-banking money lenders, etc.
As to the non-banking money lenders, the FSA will examine their compliance with the legal ceilings on interest rates and the regulations for the way of collection of loans. Moreover, the FSA will examine whether they make excessive loans in accordance with the revised Guideline for Supervision.
As to the issuers of prepaid cards, the FSA will examine the adequacy of their security deposits for issuance of prepaid cards.
(6) Government financial institutions and the Japan Post
As to the government financial institutions and the Japan Post, under the circumstances their reform is developing, the FSA will conduct their inspections, taking account of their unique characters yet in line with the Inspection Manuals for private financial institutions.
II. Basic Plan for Financial Inspections
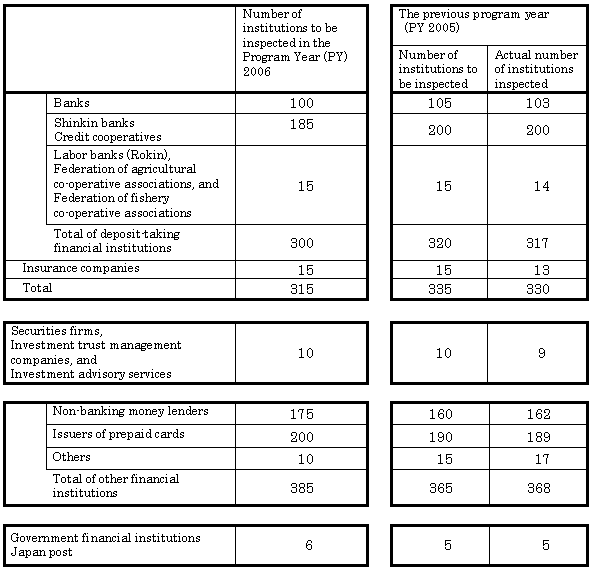
Note:
(1) These inspection numbers may be changed as necessary.
(2) Figures on the ''Banks'' are the aggregated numbers of inspected banks and inspected bank holding companies. Those of ''Insurance companies'' are also the aggregated numbers of inspected insurance companies and inspected insurance holding companies.
Site Map
- Press Releases & Public Relations
- Press Releases
- Press Conferences
- Official Statements
- FSA Weekly Review & ACCESS FSA
- Speeches
- For Financial Users
- Others
- Archives
- Laws & Regulations
- Name of Laws and Regulations(PDF)
- Recent Changes (Legislation, Ordinances, Guidelines)
- Guidelines
- Financial Instruments and Exchange Act
- Financial Monitoring Policy
- Public Comment
- No-Action Letter System
- Procedures concerning Foreign Account Management Institutions
 Search
Search


