|
 |
Minister Nakagawa speaking at the Meeting for Exchange of Views for Smooth Financing of Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises (October 15) |
Senior Vice Minister Tanimoto speaking at the meeting of the 1st Subcommittee, Financial System Council (October 15) |
Statements, Speeches & Material
In this corner, we post statements and speeches made by the Minister, the Senior Vice Minister, the Parliamentary Secretary and FSA officials, as well as presentation material they used.
Speeches
Summary of Remarks by Shoichi Nakagawa, Minister of Finance and Minister of State for Financial Services, at the Committee on Financial Affairs of the House of Representatives, the 170th Extraordinary Diet Session
Statement by Shoichi Nakagawa, Minister of Finance and Minister of State for Financial Services
"Global financial crisis and Japan's experience in the 1990s" Keynote speech by Takafumi Sato, Commissioner, Financial Services Agency, at the Symposium on Building the Financial System of the 21st Century
Photograph Gallery
In this corner, we post photographs of the Minister, the Senior Vice Minister, the Parliamentary Secretary and FSA officials at work in meetings, conferences and other events.
 |
 |
Minister Nakagawa speaking at the Japan National Press Club (October 31) |
|
 |
 |
Minister Nakagawa speaking |
Senior Vice Minister Tanimoto speaking |
 |
Parliamentary Secretary Uno speaking |
|
Meeting of Director-Generals of Local Finance Bureaus (October 30)
|
[Featured]
On October 10, 2008, the G7 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors met in Washington, DC. From Japan, Shoichi Nakagawa, the Minister of Finance and Minister of State for Financial Services, and Masaaki Shirakawa, the Governor of the Bank of Japan, attended. At the meeting, the G7 agreed to take decisive action and use all available tools, and issued a Plan of Action consisting of five action items.
Accordingly, Minister Nakagawa following his return from the United States, issued a Minister's Statement on October 14, outlining the measures to be implemented in Japan in line with the G7 plan of Action.
Furthermore on October 27, Prime Minister Taro Aso told Minister Nakagawa and other related cabinet members, to execute measures aimed at assuring market stability and facilitating financing asking them to implement the measures from the three standpoints of stock market stability, further reinforcement of financing functions and expansion in the breadth of securities investment. (This has been incorporated into the Japanese government's Economic Policy Package: Measures to Support People's Daily Lives announced on October 30.)
In response to these developments, the Financial Services Agency has taken immediate action on measures that do not require revision of laws and ordinances, etc., and at the same time has commenced work to take swift action on other measures.
The direct impact of conditions in the global financial markets on the health of Japan's financial system has been relatively limited, compared to the impact on those of the United States and Europe. Furthermore, Japan has sufficient safety nets already in place, mainly in the form of the deposit insurance system, having experienced its own financial crisis already in the 1990s. However, as the impact of the financial market turmoil around the world begins to be felt in our domestic financial sector through stock prices and conditions in the real economy, it has been decided that measures should be implemented in an urgent manner, placing emphasis on swift and appropriate action, while continuing to monitor developments on heightened alert.
The measures announced on October 14 and 27 are outlined as follows.
[Measures for stabilizing the stock market]
1. Relaxation market restrictions regarding purchase of own stocks by listed companies
From the viewpoint of preventing market manipulation, purchase of own stocks by listed companies is subject to the following four restrictions under the Cabinet Office Ordinance:
(i) Volume of purchase per day. The upper limit is 25 percent of average daily trading volume during the four weeks immediately preceding the purchase.
(ii) Timing of purchase. Purchase during the 30 minutes immediately before the close of trading is prohibited.
(iii) Purchase price. The price cannot exceed that of the most recent sales.
(iv) Number of securities firms. Purchase is permitted through only one securities firm per day.
In light of the current condition of Japan's stock markets, the restrictions regarding (i) the upper limit on the volume of purchase per day and (ii) the timing of purchase will be temporarily relaxed in order to facilitate the purchase of own stocks by listed companies.
2. Strengthening of restrictions on short selling
In Japan, the following restrictions with regard to trading of all listed stocks have already been in place and continue to be in effect today:
1) Verification and marking requirement
Traders are required to verify and mark whether or not the transactions in question are short selling.
2) "Uptick rule requirement"
Short selling transactions are prohibited, in principle at prices no higher than the latest market price announced by the stock exchange concerned.
In response to the Minister's Statement of October 14, the FSA has decided to take the following additional measures:
(i) Enhancement of disclosure on information regarding short selling at the exchanges
From the viewpoint of ensuring market transparency and facilitating the monitoring of market activities, the FSA requested exchanges to enhance their disclosure on information regarding short selling. Specifically, starting from October 14, exchanges are requested to make daily announcements on their aggregate price of short selling regarding all securities and aggregate price of short selling by sector (33 sectors in total), although monthly announcements had been previously made on their aggregate price of short shelling regarding all securities.
In response to the Prime Minister's order of October 27, the FSA has taken the following measures, which are urgent and temporary steps effective until March 31, 2009, in view of the current state of the stock markets and other developments, including new restrictions on short selling in foreign countries.
(ii) Naked short selling (short selling in which stocks are not borrowed at the time of selling) is prohibited
(iii)Holders of a short position of a certain level or more are required to report to exchanges through securities firms, and exchanges are required to publicly disclose such information
* Details on 1 and on (ii) and (iii) of 2 are found in "Explanations of Laws and Regulations" of the current issue of Access FSA. For details on (i) of 2, please access FSA requests enhancement of disclosure on information regarding short selling at the exchanges (October 14, 2008) under Press Releases section on the FSA website.
3. Flexible management of stock ownership restriction on banks
Although stock ownership by banks, etc. is regulated to not exceed the value of Tier 1 capital under the Act on Limiting Shareholding, etc by financial institutions, etc. (Act No. 131, 2001), the Act allows ownership exceeding Tier1 capital as an exception with the approval of the authorities, if it is a result of unforeseeable events, including a rise in shock market prices. With this latest measure, ownership exceeding the Tier 1 capital may be tolerated with supervisory approval in view of the current market conditions. The measure is already in effect.
[Measures for further strengthening of financial functions]
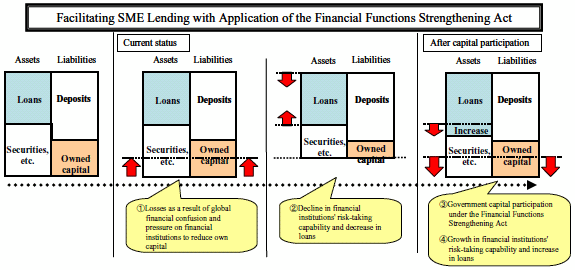
4. Facilitating SME financing by strengthening and utilizing the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions
The objective of the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions (Act No. 128, 2004) is to strengthen financial functions through government capital participation in financial institutions and to stimulate regional economies, including facilitating lending to small- and medium-size enterprises (SMEs).
The Minister's Statement of October 14 outlined the urgent need to facilitate financing to SMEs by regional financial institutions by strengthening and utilizing the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions, as part of the measures aimed at implementation of the G7 Plan of Action.
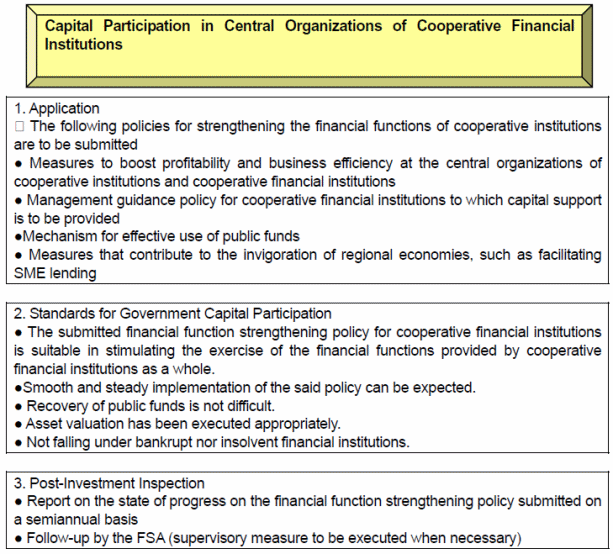
Accordingly, the Bill for Amendment of the Act on Special Measures for Strengthening Financial Functions and the Act on Special Measures for Promotion of Organizational Restructuring of Financial Institutions was approved by the Cabinet on October 24, 2008, and has been submitted to the Diet. In this bill, it is proposed that the deadline for application pertaining to capital participation by the government be extended to March 31, 2012, and the capital participation requirements be revised. Also, the creation of a new scheme for capital participation of the government in central organizations in order to promote enhancement of the financial functions provided by those of cooperate financial institutions as a whole.
In addition, the upper limit of the government guarantee for borrowings by the Deposit Insurance Corporation for the purpose of capital participation by the government, which is currently ¥2 trillion (FY 2008 budget), is scheduled for review for a possible increase to a level adequate for facilitating financial functions further, according to the Measures to Support People's Daily Lives announced on October 30.
 |
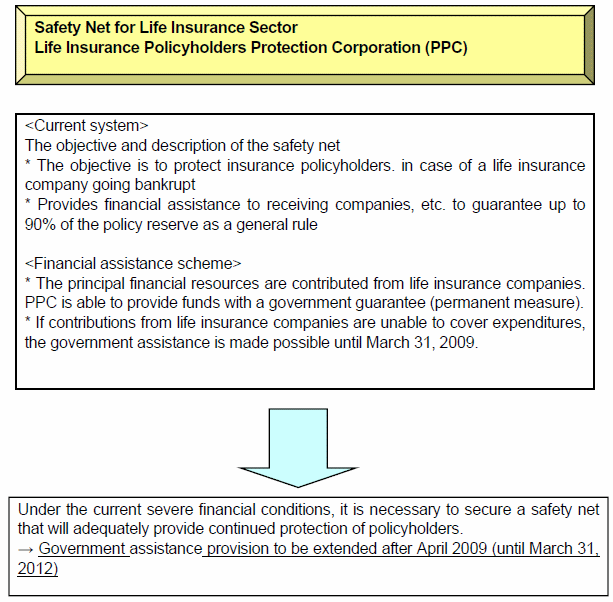
5. Extension of government assistance for the safety net with regard to life insurance sector
As a safety net for life insurance sector, a scheme is already in place for financial and other assistance by the Life Insurance Policyholders Protection Corporation (PPC) (established in December 1, 1998), to ensure the protection of insurance policyholders if a life insurance company enters bankruptcy. It provides a guarantee of up to 90% of the policy reserves to be accumulated by the insurance company for the payment of insurance claims (actuarial liability) as the general rule.
The financial resources of PPC are covered by contributions from life insurance companies. However, if such contributions alone are unable to cover expenditures, government assistance is made possible until March 31, 2009, under the current law.
The Minister's Statement of October 14 states that consideration will be given to extending government assistance for the safety net even after the current deadline of March 31, 2009. Following this statement, the bill for amendment of the Insurance Business Act was approved by the Cabinet on October 24, 2008, and has been submitted to the Diet. The bill is targeted to extending government assistance until March 31, 2012, in order to ensure that the safety net will remain in place to protect the interest of insurance policyholders under the severe financial conditions.
 |
6. Partial relaxation of the capital adequacy requirement for banks
In order to maintain the financial soundness of banks and other deposit-taking financial institutions, these institutions are required to keep regulatory capital at a certain ratio to assets weighted by risk (capital adequacy requirement). In calculating the capital adequacy ratio (e.g. for international standards), part of valuation profits in accounting from available-for-sale securities, such as stocks and bonds, are permitted to count in regulatory capital calculation.
Based on the Measures to Support People's Daily Lives that aims to "allow more flexibility into the capital adequacy requirements in compliance with the framework of international accord so as not to weaken financial intermediary functions of financial institutions as a result of abrupt fluctuations in capital adequacy ratio under the ongoing extraordinary market turmoil, " the FSA will take the following supervisory measures to be in effect for a limited period from the business year ending December 2008 to the business period ending March 2012. Accordingly, the proposed FSA Regulatory Notice will be issued by the FSA shortly for public comment.
(1) Deposit-taking financial institutions to which domestic standards are applied (financial institutions that are not operating overseas) are not required to recognize valuation losses from available-for-sale securities deducted from the Tier 1 capital.
(2) Deposit-taking institutions to which international standards are applied (financial institutions with overseas operations) will have an option not to recognize both valuation profits and valuation losses specifically on securities without credit risks (zero-risk-weighted securities), such as government bonds, in capital calculation.
(Summary of Relaxation Measure)
| Previous | New | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic standards |
Government bonds, etc. |
Valuation profits: Excluded from capital adequacy Valuation losses: Approx. 60% (after tax basis) deducted from Tier 1 |
(Valuation profits: No change) Valuation losses: Excluded from capital calculation |
| Stocks, corporate bonds, etc. |
|||
| International standards |
Government bonds, etc. |
Valuation profis: 45% included in Tier 2 Valuation losses: Approx. 60% (after tax basis) deducted from Tier 1 |
Valuation profits: Excluded from capital calculation Valuation losses: Excludedfrom capital calculation |
| Stocks, corporate bonds, etc. |
(No change for both valuation losses/profits) |
7. Support for efforts toward optimal accounting of financial products
Study and work are currently underway in developing accounting standards, including accounting for financial products, at the Accounting Standards Board of Japan (ASBJ), with attention focused on international development. The FSA policy is to provide support and work toward the development of adequate accounting for financial products, with attention to the Prime Minister's instructions of October 27 and the Measures to Counter Difficulties in People's Daily Lives.
Greater clarity in fair-value calculation method
In financial products accounting, calculation is to be based on "fair value," excluding certain cases. Under this accounting system, the market value is defined as "fair value" if there is adequate trading in the market. If market price does not exist, on the other hand, a value based on logical calculation (theoretical value) is employed as "fair value."
Regarding this, ASBJ announced in its Q&A of its interpretation that, when market price cannot be adopted as it is in accounting, such as when actual transactions are extremely small in number or when there is an extremely wide difference in "bid" and "offer" prices, these are cases where it is appropriate to employ the theoretical value should be employed as "fair value."
In response to clarification of the rule by ASBJ, the FSA revised its Basic Policy for Financial Inspections in Program Year (PY) 2008 to conduct verification of self inspection of negotiable securities by financial institutions with attention to this interpretation. Verification with attention to further clarification of accounting standards, etc. in the future was also included explicitly in the Policy.
Change in objective of financial products ownership
The ASBJ is conducting studies into the approval, in very exceptional cases, of the reclassification of securities in the "trading securities" or "other securities" categories included in fair-value assessment into the "held-to-maturity securities" category, which is excluded from fair-value assessment (amortized cost method). The FSA is in full support of swift action by the ASBJ.
8. Other activities for facilitating financing
The FSA has been working in cooperation with the Small and Medium Enterprise Agency in order to gain a detailed assessment of actual conditions regarding SME financing. On October 15, Minister Nakagawa issued a renewed request to representatives of financial institutions to boost smoother financing. (For a look into the request, please see the cover of the current Access FSA issue.)
Moreover, in the drive to strengthen the surveillance and facilitation of SME financing, a new information gathering service on financing by financial institutions, which reports directly to the Minister, named "Daijin Meyasubako," was created on October 16.
[Measures for expanding the breadth of securities investments]
9. Measures for facilitating stock purchase by Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans
Currently, Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans are exempted from certain securities regulations such as insider trading restrictions, under the following conditions:
1) Amount of employee contribution to the employee stock ownership plan is less than one million yen per person per one contribution (there are no restrictions on the total outstanding amount of contribution); and
2) Stocks are purchased continuously in accordance with a certain plan, and not based on individual investment decisions.
In order to facilitate stock purchase by Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) made the following requests today to the Japan Securities Dealers Association (JSDA):
(i) From the viewpoint of promoting active use of Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans, the JSDA should promote understanding of the conditions mentioned in 1 above through its members; and
(ii) With respect to the JSDA guideline which states that "stock purchase in accordance with a certain plan" must be conducted, in principle, on a specified date of the month, the JSDA should clarify that stock purchase does not necessarily need to be conducted on one specified date per month, but can be conducted on two or more specified dates.
In order to facilitate stock purchase by Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) made, at the instruction of the Prime Minister, two requests to the Japan Securities Dealers Association (JSDA) on October 27 as follows: From the viewpoint of promoting active use of Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans, the JSDA should promote understanding of the above exemption through its members; and the JSDA should clarify that stock purchase does not necessarily need to be conducted on one specified date per month, but can be conducted on two or more specified dates.
* For further details, access Measures to facilitate stock purchase by Japanese-style employee stock ownership plans (27 October, 2008) under "Press Releases" in the FSA website
[International Affairs]
Publication of "Report of the Financial Stability Forum (FSF) on Enhancing Market and Institutional Resilience: Follow-up on Implementation" by the Financial Stability Forum
The Financial Stability Forum (FSF) submitted a report titled Report of the Financial Stability Forum on Enhancing Market and Institutional Resilience (hereinafter referred to as the "April Report") to the Meeting of the Group Seven Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors (G7) held this April in Washington, DC on April 11, 2008. The report consisted of analysis of the causes of the recent global financial market turmoil and proposals on concrete, comprehensive market reinforcement measures. The FSF reported on the state of implementation of the proposals in the April Report at the G7 meeting held on October 10 (2008) in Washington, DC, and published the Report of the Financial Stability Forum on Enhancing Market and Institutional Resilience: Follow- Up on Implementation (hereinafter referred to as the "Follow-Up Report").
The Follow-Up Report reported in detail on the state of implementation of all of the proposals in the April Report. In addition, it presented proposals that should be implemented with greater speed, as well as additional matters that should be addressed in the future. The report can be outlined as follows.
1. State of Implementation of the Proposals in the April Report
» National financial authorities, international organizations and private sector bodies are currently working on implementation of the proposals in the April Report, in the following five areas.
- Strengthening prudential oversight of capital, liquidity and risk management
- Enhancing transparency and valuation
- Changes in the role and uses of credit ratings
- Strengthening authorities' responsiveness to risks
- Robust arrangements for dealing with stress in the financial system
» The work on priority actions designated in the G7 statement in April to be implemented within 100 days has been carried out as planned. Actions endorsed for implementation by the end of 2008 are expected to produce concrete results by then. Work is also on track to implement many other recommendations, and will be monitored for swift action on these recommendations.
» In light of market developments, implementation will be accelerated in the following areas.
- Market participants to set up central counterparty clearing for OTC credit derivatives.
- Accounting standards-setters to enhance and converge guidance on valuation of instruments in inactive markets, as well as accounting and disclosure standards for offbalance sheet activities.
- Credit rating agencies (CRAs) to enhance their efforts to provide differentiated information or ratings for securitized products.
- Private sector organizations that have recommended improvements to industry practices are to establish frameworks for rigorously monitoring and reporting on the timely implementation of such improvements.
2. Additional Issues to Be Addressed
» Along with the proposals in the April Report, the FSF will also address the following additional issues.
- Study and monitor the international interaction and consistency of emergency response measures currently being implemented by national bodies.
- Study and address pro-cyclicality in the financial system. The following issues are to be reported at the G7 meeting next April.
-Capital regime: The impact of Basel II on the cyclicality of capital requirements will be examined, along with measures to strengthen capital buffers during periods of economic prosperity.
-Loan loss provisioning: Study into how judgment is used in accounting standards from a long-term perspective, for provisioning unaffected by economic conditions.
-Compensation arrangements in financial institutions: Study into the appropriate role for regulators and supervisors in this area.
-Valuation and leverage: Analysis of the interplay between valuation and leverage and study into policy responses.
- Scope of financial regulation to be reassessed, with an emphasis on institutions, instruments, etc. that are currently unregulated.
- Integration of macroeconomic oversight and prudential supervision to translate systemic concerns more effectively into concrete supervisory and regulatory responses.
To date, the FSA has been taking swift and aggressive action on the proposals in the FSF Report, from the perspective of strengthening information disclosure by Japan's financial institutions, as well as risk management. Furthermore, the FSA is participating in, and actively contributing to discussions and deliberations by various international bodies regarding the proposals, those bodies are implementing. The FSA will continue to work in close cooperation with the relevant international bodies and in order to implement the FSF proposals effectively.
Note: The Financial Stability Forum (FSF) was established in 1999 by the finance ministers and central bank governors of the Group Seven countries, for the purpose of exchanging information on financial market oversight and surveillance and promoting greater stability in international finance through closer international cooperation. The FSF membership consists of the relevant authorities in nations and territories where important international finance centers are located, along with international bodies including financial oversight administrators (Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) and International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS)), international financial bodies (International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank) and others. Japan is represented by the Financial Services Agency, Ministry of Finance and Bank of Japan.
The 4th Meeting of the International Forum of Independent Audit Regulators (IFIAR) was held in Cape Town, South Africa. Chairman Akira Kaneko of the Certified Public Accountants and Auditing Oversight Board participated in the meeting.
The IFIAR is an association of audit regulators established to promote cooperative relations and share auditing experiences between various countries, for the betterment of auditing quality. At present, it consists of 27 nations and territories including the US, UK and other leading countries (as members) and 8 international organizations (as observers).
At the meeting, the IFIAR Charter drawn up at the 3rd meeting in Toronto was adopted by the members. The Charter laid out the organization and future role of the IFIAR, specifically confirming the body's activities as: sharing knowledge gained from practical experience in auditing by the audit regulators of member nations; promoting collaboration in regulatory activities; and providing a platform for dialogue with other organizations that have an interest in audit quality. It also specified how the organization would be developed, including the establishment of an Advisory Council, etc.
Furthermore, there were exchanges of views on audit regulation organizations, such as the registration and notification of foreign audit firms, etc., and on information regarding audit quality. Discussions were also held with representatives of BDO, Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu and KPMG, three of the six major international audit networks.
The IFIAR also decided to hold its third annual audit inspection workshop, for members to exchange skills and experiences in regulatory auditing, on February 12-13, 2009 in Stockholm.
The CPAAOB plans to continue to participate in these meetings and to work for the further improvement of audit trustworthiness and better audit quality in Japan, by building and strengthening cooperation and collaborative ties with audit regulators in other countries.
 |
Chairman Kaneko (second from right)
Site Map
- Press Releases & Public RelationsPage list Open
- Press Releases
- Press Conferences
- Official Statements
- FSA Weekly Review & ACCESS FSA
- Speeches
- For Financial Users
- Others
- Archives
- Laws & RegulationsPage list Open
- Name of Laws and Regulations(PDF)
- Recent Changes (Legislation, Ordinances, Guidelines)
- Guidelines
- Financial Instruments and Exchange Act
- Financial Monitoring Policy
- Public Comment
- No-Action Letter System
- Procedures concerning Foreign Account Management Institutions
 Search
Search