 |
 |
Minister Yosano receiving an opinion statement from Chairman Ando at the General Meeting of the Business Accounting Council (April 9) |
Senior Vice Minister Tanimoto speaking at the Meeting of Director-Generals of Local Finance Bureaus (April 23) |
[Topics]
[International Affairs] |
[Topics]
At the joint meeting of the 20th Audit Committee Meeting and the General Meeting of the Business Accounting Council, which was held on April 9, 2009, after deliberations on the revision of the Auditing Standards, the “Opinion on the Revision of Auditing Standards” was put together and was handed from Chairman Hideyoshi Ando (professor at Senshu University) to the Minister for Financial Services, Kaoru Yosano.
The latest revisions of the Auditing Standards reviewed those standards that relate to the explanatory notes regarding the going concern assumption (see Note), from the perspective of providing investors with more useful information, and taking international consistency into account.
Note: In corporate accounting, profits and losses etc are calculated for a certain period of time based on the going concern assumption (the assumption that an entity will continue its business for a reasonable period of time).
Under the previous provisions, it was understood that whenever certain events or conditions existed, such as the occurrence of successive operating losses or the breach of a financial covenant, explanatory notes concerning the going concern assumption needed to be included automatically in the financial statements. Taking consistency with international standards into account, it was decided to revise these provisions. Specifically, it was decided that, having evaluated management’s assessment and plans for future actions to deal with these events or conditions, in the event a material uncertainty is found related to the going concern assumption, auditors would determine whether appropriate explanatory notes had been provided by management.
Furthermore, given that the semi-annual auditing standards and quarterly review standards also contain similar provisions regarding the going concern assumption, the Audit Committee of the Business Accounting Council also plans to consider revisions of these standards from a similar perspective.
The revised Auditing Standards will be effective for audits of financial statements for periods ending on or after March 31, 2009. (Public consultation on the Cabinet Office Ordinance for Partial Amendment of the Regulations on Terminology, Format and. Preparation Method of Financial Statements, etc. were issued on April 20, 2009 by the Financial Services Agency, and the ordinance was promulgated and brought into force.)
*For further details, access Publication of Position Paper by Business Accounting Council (April 10, 2009) under “Press Releases” on the FSA website.
Audit Procedures Related to the Going Concern Assumption
Comparison between Japan and the US/Europe concerning
Explanatory Notes regarding the Going Concern Assumption
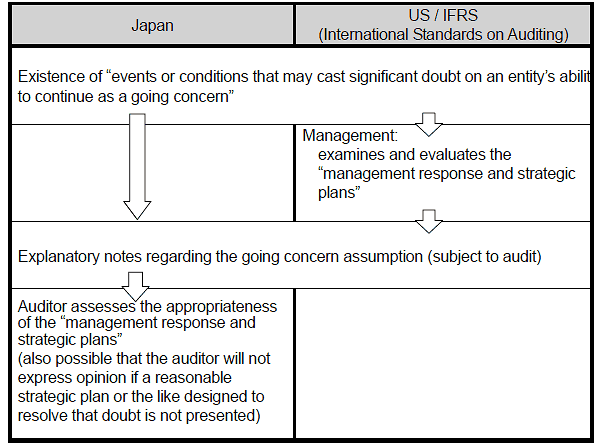
 Examples of “events or conditions that may cast significant doubt on an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern”
Examples of “events or conditions that may cast significant doubt on an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern”
- Occurrence of successive operating losses, etc.
- Breach of a financial covenant
- Difficulties in repaying debt, etc.
| Japan | US / IFRS (International Standards on Auditing) |
|---|---|
|
|
Note: Revisions expected in the US.
On March 31, the Certified Public Accountants and Auditing Oversight Board (CPAAOB) issued the “Business Year 2009 Basic Plan for Examinations and Basic Plan for Inspections.” An outline of the basic plans is as follows.
The CPAAOB was established in April 2004 for the purpose of improving and strengthening the certified public accountant and auditing system. On receipt of “Quality Control Review” reports from the Japanese Institute of Certified Public Accountants (JICPA), the CPAAOB examines the content of the reports, and where necessary, conducts on-site inspections at JICPA or at the audit firms.
CPAAOB has already set down its basic policy on examinations and inspections between the 2007 and 2009 business years in the document entitled “For Further Improvements of Audit Quality: Basic Policies on Quality Control Reviews (June 2007).” Each business year, in addition to revising the basic policies, the CPAAOB also formulates a “Basic Plan for Examinations” and a “Basic Plan for Inspections.” (The CPAAOB formulates these plans according to the April-March business year.)
In business year2009, in view of the status of notifications made by foreign audit firms and the details of those notifications, the CPAAOB made necessary amendments to the policies regarding the response to foreign audit firms described in the Basic Policies on Examinations. Furthermore, in view of the basic line of thought shown in the policies, the CPAAOB has also formulated and released the “Business Year2009 Basic Plan for Examinations and Basic Plan for Inspections.”
1. Basic Plan for Examinations
With regard to the development status of quality control systems in audit firms, the CPAAOB will focus on examining the status of development particularly at sole practitioners. The CPAAOB will also continue to focus on examining the monitoring of the quality control of audits. Furthermore, the CPAAOB will also examine the operational status of the JICPA’s Registration System for Listed Company Audit Firms.
2. Basic Plan for Inspections
In view of the results of JICPA’s quality control reviews, where necessary, the CPAAOB will inspect large audit firms and small and medium scale audit firms.
3. Response to foreign audit firms
With regard to foreign audit firms, in view of the status of notifications made to the Financial Services Agency (FSA) and the details of those notifications, the CPAAOB will work on enhancing its coordination and cooperation with relevant agencies and its relationships with foreign audit regulators, and will endeavor to collect and analyze information on the quality control of the foreign audit firms. Furthermore, the CPAAOB will scrutinize their inspection methods and so forth in detail, and where necessary, will conduct its own inspections.
[International Affairs]
Monitoring Board meets with the International Accounting Standards Committee Foundation (IASCF) Trustees
The Monitoring Board is comprised of securities regulators, including the FSA. On April 1, 2009, the Monitoring Board met for the first time with the Trustees of the International Accounting Standards Committee Foundation (IASCF) in London. The members of the Monitoring Board also elected Hans Hoogervorst as chairman. Chairman Hoogervorst represents the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) Technical Committee (Vice Chairman of the Technical Committee), and is the Chairman of the Board of the Authority for the Financial Markets of the Netherlands.
![]() Press Release on the First Meeting of the Monitoring Board
Press Release on the First Meeting of the Monitoring Board
Establishment of the Monitoring Board: Background and Developments
«Background»
The International Accounting Standards Committee Foundation (IASCF) is an independent private-sector organization, and is the parent foundation of the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) which sets the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The IASCF was established in 2000 by the International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC), which is the predecessor of the IASB. The Trustees of the IASCF set the strategies, appoint members, and manage the budgets and finance of the IASB. Currently there are two Japanese serving as IASCF Trustees: Mr. Noriaki Shimazaki (Executive Vice President, Sumitomo Corporation) and Mr. Tsuguoki Fujinuma (Immediate Past Chairman and President of the Japanese Institute of Certified Public Accountants).
The IFRS, which are set by the IASB, are one of the key infrastructures of the world’s capital markets. They affect a wide range of groups, such as preparers of financial statements, auditors and investors. Accordingly, these financial reporting standards need to take a balanced view of the opinions of all stakeholders. Further, the IASCF and IASB must avoid changing any financial reporting standards under the influence of any specific groups only. Ever since the IFRS were adopted by the European Union (EU) in 2005, they began to spread rapidly around the world; and at present they have either been adopted or allowed in more than 100 countries. Given this, the issue of ensuring the reliability of the IFRS was regarded as particularly urgent.
«Proposal by the Authorities»
On November 7, 2007, the FSA, in conjunction with the IOSCO, the European Commission (EC) and the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), proposed changes to enhance the governance of the IASCF, and proposed the establishment of a monitoring board (called a “Monitoring Body” at the time).
Furthermore, on June 18, 2008, ahead of the IASCF roundtable, the FSA, the IOSCO, the EC and the US SEC jointly announced the next steps for the creation of the Monitoring Board (called the “Monitoring Group” at the time), and made recommendations to the IASCF.
«Recommendations of the G-20 Summit»
The Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy, or so-called G-20 Washington Summit, was held in November 2008. The joint declaration of the summit included an instruction to cabinet ministers to “review the mandates, governance, and resource requirements of the international financial institutions.” The Action Plan, which was simultaneously announced, also included the following measure to be completed by March 31, 2009: “With a view toward promoting financial stability, the governance of the international accounting standard setting body should be further enhanced, including by undertaking a review of its membership, in particular in order to ensure transparency, accountability, and an appropriate relationship between this independent body and the relevant authorities.” These words signify the fact that the world leaders recognized that governance reform of the international accounting standard-setting body is an urgent issue for overcoming the financial crisis.
Link to the Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy (Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan)
«Revision of the IASCF Constitution and its First Meeting»
In January 2009, the IASCF revised its constitution, and announced the building of a formal institutional relationship with the Monitoring Board. As a consequence, this has enabled the Monitoring Board to begin activities for monitoring the IASCF, as a formal organization. The first meeting was held in London on April 1, 2009, at which Hans Hoogervorst was elected to serve as chairman. The Monitoring Board held a joint session with the IASCF Trustees, and discussions included the reconstitution of the Standards Advisory Committee (SAC), the IASB’s response to the financial crisis, and the role of the International Financial Reporting Standards in the economies of emerging nations.
Monitoring Board Members and Mission
«Monitoring Board Members»
The first members of the Monitoring Board are comprised of representatives from the following organizations: the FSA, the US SEC, the IOSCO Emerging Markets Committee and the IOSCO Technical Committee. The Monitoring Board member from Japan is the FSA Commissioner. Furthermore, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) also participates as an observer.
«Monitoring Board Mission»
The mission of the Monitoring Board is described in its Charter as follows.
- To cooperate to promote the continued development of International Financial Reporting Standards as a high-quality set of global accounting standards;
- To monitor and reinforce the public interest oversight function of the IASCF, while preserving the independence of the IASB. In that regard:
- To participate in the selection and approval of the IASCF Trustee appointments; and
- To advise the IASCF Trustees with respect to the fulfillment of their responsibilities, in particular with respect to regulatory, legal and policy developments that are pertinent to the IASCF’s oversight of the IASB and appropriate sources of IASCF funding;
- To discuss issues and share views relating to International Financial Reporting Standards, as well as regulatory and market developments affecting the development and functioning of these standards;
The FSA will actively participate in the Monitoring Board so that the IASCF and the IASB can fulfill their responsibilities from the perspective of public interest oversight.
Link to the Charter and other information on the Monitoring Board (English)
(http://www.iasb.org/News/Press+Releases/Press+release+from+IASC+Foundation+Monitoring+Board.htm![]() )
)
Significance of the Monitoring Board
The creation of a relationship with the Monitoring Board as a result of the revisions to the IASCF Constitution has been seen as progress in the governance reforms of the IASCF as an international accounting standard-setting body. The next meeting of the Monitoring Board is scheduled for July 2009.
*For further details, please refer to “Monitoring Board Meets With IASCF Trustees” (April 3, 2009) in the “Press Releases” section of the Financial Services Agency website.
This section provides information regarding the hot topics of the moment, selected from questions and answers given at the Minister's press conferences, etc.
If you wish to find out more, we invite you to visit the “Press Conferences” section of the FSA website.
Q : I understand that, together with the Prime Minister, you are leaving for London today. Some people think that, since as many as 20 countries participate in the G-20 summit, it is difficult to lead discussions to a conclusion. Could you tell us with what stance Japan will participate in the meeting and what conclusion you would like to reach?
A. To my mind, Japan’s stance has not changed at all since Prime Minister Aso visited Washington late last year. To deal with the global economic and financial crisis, it is necessary that individual countries cooperate with each other, rather than acting separately. Japan’s resolve to make the greatest possible contributions to the international community under the framework of international cooperation remains unchanged.
I believe that countries around the world share the recognition that it is necessary to build a new framework of oversight and regulation of financial transactions. Although it may take time, the Japanese government strongly feels the need to do it so as to prevent a recurrence (of a financial crisis).
(Extract from the press conference on March 31, 2009)
Q : I understand that the Financial Services Agency formally notified banks of an intensive inspection yesterday. Could you explain the purpose of the inspection again and tell us what actions the FSA will take if problems are found.
A. This inspection is intended to examine whether individual financial institutions are properly exercising their financial intermediary function. The inspection is not aimed at examining any particular bank because of concerns about management conditions but at checking, from the standpoint of a caring guardian, whether banks are conducting business based on the Banking Act.
(Extract from the press conference on April 7, 2009)
[Information]
The FSA has started an E-mail Information Service. If you register your e-mail address on the Subscribe Page of the FSA website, we will notify you by e-mail once on each day when new information is posted on our website. For details, please access Subscribing to E-mail Information Service of the FSA website.
Site Map
- Press Releases & Public RelationsPage list Open
- Press Releases
- Press Conferences
- Official Statements
- FSA Weekly Review & ACCESS FSA
- Speeches
- For Financial Users
- Others
- Archives
- Laws & RegulationsPage list Open
- Name of Laws and Regulations(PDF)
- Recent Changes (Legislation, Ordinances, Guidelines)
- Guidelines
- Financial Instruments and Exchange Act
- Financial Monitoring Policy
- Public Comment
- No-Action Letter System
- Procedures concerning Foreign Account Management Institutions
 Search
Search




